U.S. stock and corporate bond markets performed extraordinarily well from the March financial shock caused by COVID-19 to the end of last month. Then, three consecutive weeks of decline in the three major stock market indexes have been followed this week by a global slump attributed to fears of new lockdowns. A period of disconnect of financial markets with the underlying real economy has culminated in a revelation of the former’s high dependency on Federal Reserve policies.
Disconnect…
From the response by the Federal Reserve (Fed) to the March shock – interest rate reduction and creation/expansion of several lines of acquisition of private assets and credit provision – the rise in stock price indices in the U.S. markets led them in August to levels higher than pre-pandemic, in turn already considered high. Meanwhile, the economic recovery, even after hitting rock bottom in the second quarter, remained partial and uncertain, with a prevailing perception that a return to the pre-crisis growth trend would not be likely. Stock prices seemed disconnected from the real economy (Figure 1, left-hand side panel).
The averages reflected in stock indexes went up with a sectoral differentiation that reflected the asymmetry of the impacts of the crisis of COVID-19: technology and health booming, not being so much the case with energy, finance and the branches of services directly impacted by the pandemic (Figure 1, right-hand side panel). Still, the whole set exhibited a revaluation performance far beyond what would be expected by looking at the real economy.
Figure 1
The vertical line in the left-hand side panel indicates February 19, 2020 (S&P 500 pre-crisis peak).
(1) Shanghai composite equity index. (2) Cumulative average growth rates of earnings per share (EPS), calculated between realized end-2019 and estimated end-2023. (3) S&P 500 constituents as of 18 August 2020, simple averages. (4) Amazon (AMZN), Apple (AAPL), Facebook (FB), Google (GOOG, GOOGL), Microsoft (MSFT), and Netflix (NFLX).
Source: BIS Quarterly Review, September 2020
A detachment from reality also seemed to be in full swing on the corporate credit side. Despite pre-pandemic fears that several companies had reached excessive levels of indebtedness in recent years, in addition to facing a drop in revenues during the crisis, credit spreads tightened (Figure 2, left-hand side panel).
According to the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) quarterly report released last week, such long-term credit margins have fallen to historically low levels, despite evidence of a deterioration in credit quality (Figure 2, right-hand side panel). The issuance of new debt across the spectrum of corporations – all ratings, but especially from companies with “investment grade” – was massive, even if partially for precautionary reasons, thereby increasing the degree of indebtedness in the capital structures of many companies.
The major responsible for such disconnection was, of course, Fed policy. Lower interest rates and asset price volatility have boosted investments in risky assets. In the case of technology companies, enthusiasm fed itself: dealers buying stocks in advance, in the expectation that prices would continue to rise, eventually reinforcing and corroborating their rise. In any case, as the BIS report points out, the appreciation in most sectors has led to ratios between stock prices and their yields to levels close to the historic top (Figure 1, middle panel). The opportunities opened by financial conditions even more favorable than before the crisis outweighed its effect on business activity in the real economy.
Figure 2
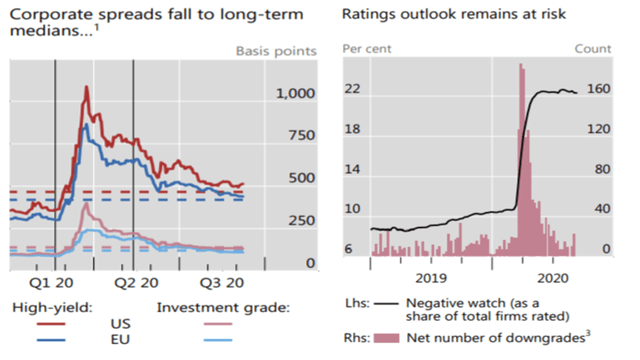
The vertical lines indicate February 19, 2020 (S&P 500 pre-crisis peak) and May 12, 2020 (Fed starts purchasing corporate ETFs). The dashed lines indicate 2005–current medians.
(1) Option-adjusted spreads.
Source: BIS Quarterly Review, September 2020
… and dependency on the Fed
Any remarkable event since late August? There was a (virtual) meeting of central bankers in Jackson Hole where Fed Chairman Jerome Powell announced a change in the monetary policy framework, something reinforced at the Fed’s own meeting last week. Instead of projecting inflation to a certain time horizon, matching it with a 2% annual rate, and making interest rate policy decisions from that, as in the previous regime, the target would now be “flexible”, aimed at an average, which would open up the possibility of waiting for some time with inflation above (below) before tightening (loosening). One may say that it is like looking at effective inflation (ex post), instead of being guided by expectation (ex ante).
Something equivalent to this would also happen regarding the consideration of unemployment rates in decision-making. A kind of confession of the failure to rely on projections of the “Philips curve” – the relationship between unemployment levels and inflation – in recent years.
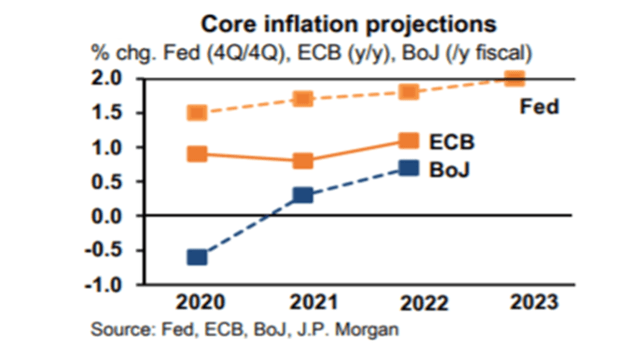
In last week’s meeting, the Fed announced a push to the bottom on the low interest rate pedal, intending to keep it there until 2023. The median inflation (core CPE) projections by committee members pointed to levels below 2% by then (Figure 3). On the other hand, there was no anticipation of specific policies regarding the purchase of assets in the “quantitative easing” (QE), which generated multiple complaints.
Figure 3
Anyone doing minimal research on what analysts are saying about September and the immediate future will find an above-normal polarization between “bullish” and “bearish”. A bullish take highlights the near-zero interest signal until at least 2023 and the mass issuance of Initial Public Offerings of shares last week to argue that “the easy money will keep fueling the market’s fever”, particularly in the case of technology companies. The past few weeks would be nothing more than a corrective pause, compounded by the Fed’s lack of commitment to continue buying long U.S. Treasury papers or other QE measures.
A bearish take, in turn, highlights the proliferation of “zombie” companies that survive via debt and will have to face the lasting changes associated with the COVID-19 crisis, as well as other aspects of the disconnect between asset prices and the underlying real economy. The BIS report drew attention to the pressures suffered by banks considered vulnerable. This week began with fears about new lockdowns due to new COVID-19 outbreaks, impacting financial markets and the global economic recovery.
The fact is that the disconnect and abrupt fluctuations in U.S. financial markets are manifesting a pronounced dependence – addiction – in relation to precise and detailed signals issued by the Fed. For its part, the Fed, by adopting a “flexible” inflation targeting regime and an announcement of low interest rates for long, signaled its recognition that it will not be able to provide financial markets with such guidance.
The role of superhero hitherto fulfilled by the Fed’s monetary policy seems to have driven it to exhaustion. Fiscal policy needs to come to its rescue.
First appeared at Policy Center for the New South
Disclosure: I/we have no positions in any stocks mentioned, and no plans to initiate any positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it. I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.





